- Details
- By Native News Online Staff
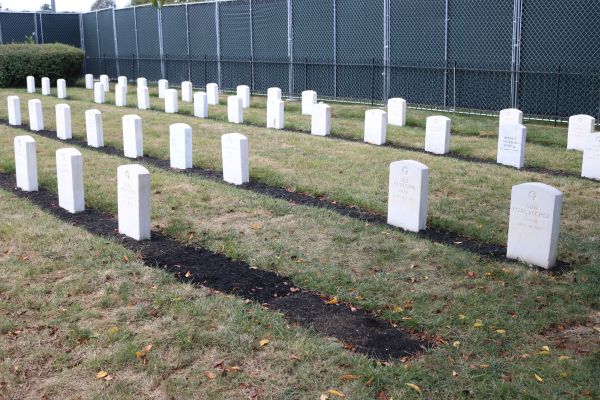
This week, the U.S. Office of Army Cemeteries began its annual process of disinterring, identifying, and returning the remains of eleven Native American children— who died more than a century ago at a government-run Indian boarding school in Pennsylvania— home to their closest living relatives.
Those former students include William Norkok from the Eastern Shoshone Tribe; Almeda Heavy Hair, Bishop L. Shield, and John Bull from the Gros Ventre Tribe of the Fort Belknap Indian Community; Fanny Chargingshield, James Cornman, and Samuel Flying Horse from the Oglala Sioux Tribe; Albert Mekko from the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma; and Alfred Charko and Kati Rosskidwits from the Wichita and Affiliated Tribes. One additional tribal nation receiving their relative's remains wishes to remain anonymous, according to a spokesperson from the Office of Army Cemeteries.
The students are among nearly 200 who died and were buried in the government’s care between 1880 and 1910 while attending the nation’s flagship Indian boarding school, Carlisle Indian Industrial School, in Carlisle, Penn.
Over the last seven years, the Army has returned 32 children’s remains back to their relatives. Each project was conducted over about a month-long period during the summer by a team of professionals from the Army Corps of Engineers’ Center of Expertise for Curation. The team worked with tribal nations to carry out the process of exhuming and identifying each child’s remains. The Army confirmed to NNO that it will be disinterring and returning an additional 18 children in 2025. This disinterment project began on September 3, 2024, and will end on October 14, according to the Office of Army Cemeteries.
In 1879, the Army’s Carlisle Barracks became the site of the nation’s first government-run Indian boarding school. Operating under the motto of “kill the Indian, save the man,” school administrators tried to forcibly assimilate 7,800 Native American children from more than 140 tribal nations through a mix of Western-style education and hard labor.
Before it closed and the property was transferred to the Army in 1918, the school buried the bodies of at least 194 Indigenous children in the school cemetery, including 14 who are marked with “unknown” grave markers.
Many students’ deaths were announced in the local newspaper at the time, noting causes of death as “that dread disease, consumption” or tuberculosis or detailing circumstances of unknown sickness.
More Stories Like This
Indian Gaming Association Condemns CFTC Over Prediction Markets, Warns of Threat to Tribal SovereigntyCommittee Advances 20% Increase to Navajo Child Support Guidelines
Navajo Committee Advances $84M Transportation Improvement Plan
NCAI Passes Two Emergency Resolutions on Immigration Enforcement Activities
Chickasaw Lighthorse Police Officer named Indian Country Law Enforcement Officer of the Year
Help us defend tribal sovereignty.
At Native News Online, our mission is rooted in telling the stories that strengthen sovereignty and uplift Indigenous voices — not just at year’s end, but every single day.
Because of your generosity last year, we were able to keep our reporters on the ground in tribal communities, at national gatherings and in the halls of Congress — covering the issues that matter most to Indian Country: sovereignty, culture, education, health and economic opportunity.
That support sustained us through a tough year in 2025. Now, as we look to the year ahead, we need your help right now to ensure warrior journalism remains strong — reporting that defends tribal sovereignty, amplifies Native truth, and holds power accountable.
 The stakes couldn't be higher. Your support keeps Native voices heard, Native stories told and Native sovereignty defended.
The stakes couldn't be higher. Your support keeps Native voices heard, Native stories told and Native sovereignty defended.
Stand with Warrior Journalism today.
Levi Rickert (Potawatomi), Editor & Publisher